Green Data Centres: Data at Scale, Impact at Zero?
Discover sustainability practices for green data centres. Learn how to scale dat…

Change is inevitable. It requires that your organisation’s codebase is sustainable and you are able to change all the things you ought to change, safely, and can do so for the lifespan of your product. That’s where SRE’s come into play. There is another uncovered sustainability aspect to software and platforms, which this blog post will dive into and show how SREs should extend their scope by one metric.
Site Reliability Engineering (SRE)
SRE is a term coined by Google to explain how they run their systems. It was Google’s answer to the importance of today's challenges with ensuring application performance and reliability at scale.
SRE is an approach that helps you build and operate more reliable, scalable, and efficient systems. SREs are responsible for the operations and maintenance of complex systems, including monitoring, logging, alerting, and incident response. They also work with developers to improve the design and architecture of systems to make them more resilient and scalable.
SRE’s at Google use the four golden signals1. These signals are considered to be the most important metrics to monitor for any system, as they provide a holistic view of its health and performance from the user's perspective.
These signals form the base of the SLIs, SLOs and SLAs.
Many companies are familiar with the concept of SLAs, but the terms SLI and SLO are new and worth explaining. SLAs are overloaded and have taken on a number of meanings depending on context.
The goal of Service Level Agreements (SLAs), Service Level Objectives (SLOs), and Service Level Indicators (SLIs) isn’t to create a legal document; it is meant to align on reliability, availability targets, and system performance.
In order to set targets you need to understand and maintain SLIs, SLOs, and SLAs.
These can be seen as hierarchical:
SLOs are the driving force of SRE teams. We have a Global SLO and that is that the temperature increase needs to stay below 1.5°C on global average (Paris Climate AGREEMENT). Current value: 1.29 °C (climateclock.net).
As described above, code sustainability is reliability over the lifespan of a product. But the missing piece is the impact a product has on our planet. This means we don’t only need to balance technical and operational tasks, but add environmental sustainability to it.
Modern software follows usually some design principles like the following, which are based on the 12factor Apps principles2:
They form a great base for performant, resilient and easy to operate apps. But they do miss the environmental sustainability aspect. We need to extend these design principles with:
How to use this in an SRE’s day-to-day job. Add a fifth golden signal to your monitoring system and create an SLI for software carbon intensity3.
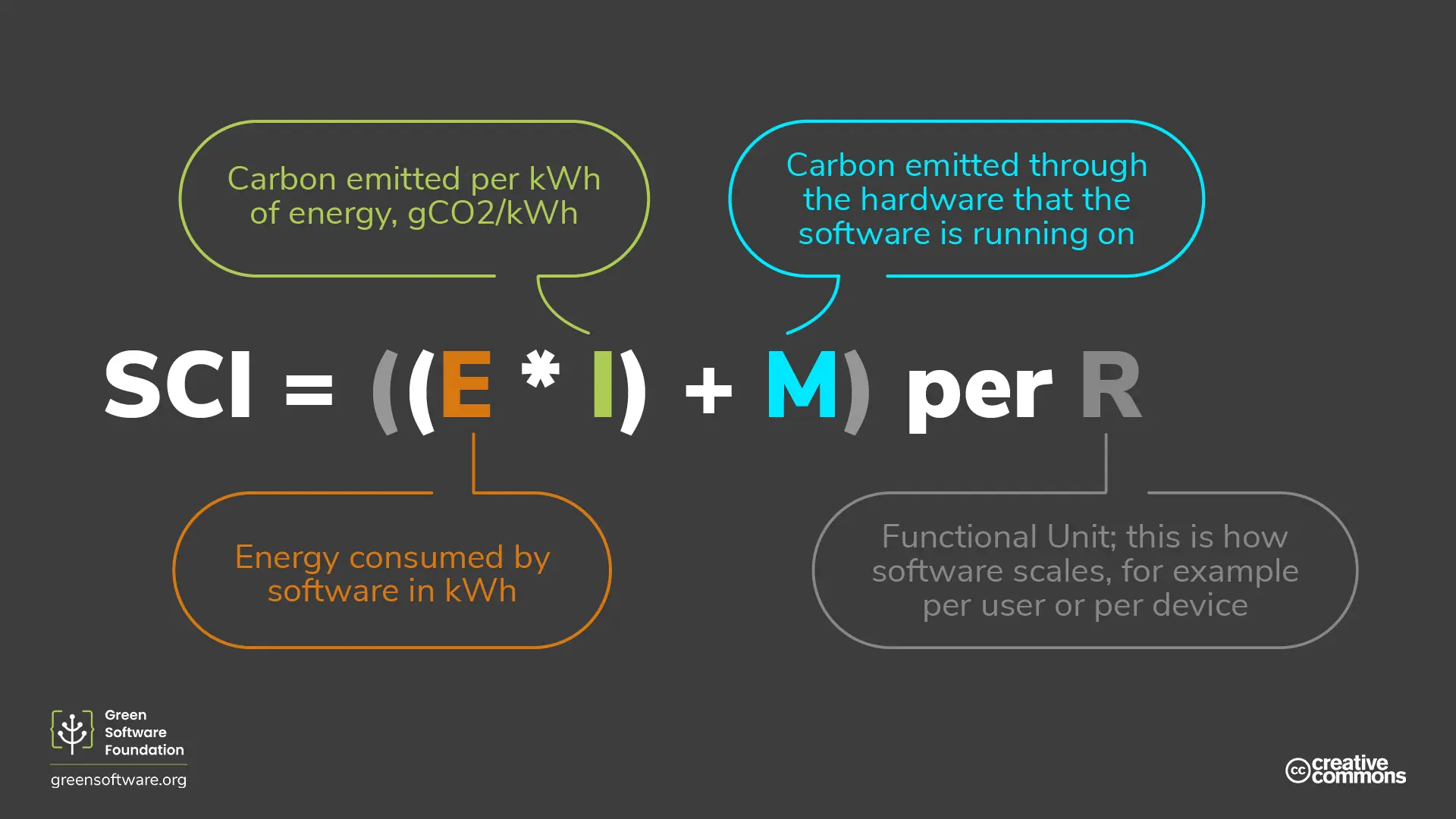
The equation itself contains four parts: Energy, Carbon Intensity, Embodied Carbon, and the Functional Unit of your system. Using these four inputs, you can accurately calculate your software’s carbon intensity. Let’s look at an example
| 1.87 kWh | Based on the CPU Type at 50% utilisation and 8W per 4GB of memory |
| 256 gCO2/kWh | Electricity Maps |
| 855 gCO2eq | embedded Carbon, subsidised 1d of 5y lifetime |
| 10 rps | requests per second |
At an average load of 50% for 24h in the Azure West Europe Region on a DB8as v4) VM the result is 0.00156 gCO2eq/R.
But how do you get these values? Here we used data based on the CPU spec which is publicly available. But you don’t want your SRE’s to do this with pen and paper. This is part of what we are currently building4 at re:cinq it does XYZ and can be used as the base for calculating automatically and continuously the SCI index.
Now you have a SLI, which is our software carbon intensity. Here it is for the given service: 1.56 emissions rate per 1,000.
Now you have the SCI, but how can we lower our software related carbon emissions?
There are many things someone can do to lower the carbon emissions and I would group the activities into two. The simple things we can do and the more complicated ones.
This can be done with some simple things like:
Do a right-sizing exercise on all your servers because everything tends to be
overprovisioned to start with.
Make use of auto-scaling at peak and scale down to the bare minimum.
Or more complicated ones:
The SCI will go down each time and you have a refined SLI. There are many more activities and things possible. The easy one will already show a huge reduction of emission and your cloud-bill, where software optimization will bring you even further, but require more work.
These actions combined is an SRE’s job. Make systems more effective over time. And if you add SCI to your signals and optimise for carbon-efficiency, your systems are faster, cheaper and more resilient because of their reduced complexity.
SREs play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of software. By measuring and optimising the carbon footprint of their systems, SREs can help to make software more sustainable and contribute to a healthier planet.

Discover sustainability practices for green data centres. Learn how to scale dat…

Explore how energy proportionality affects server efficiency and sustainability.…

Discover the 'Follow the Sun' strategy for greener IT. Learn to optimize workloa…
Get a shared vocabulary of proven Transformation Patterns, common Anti-Patterns, and Paradigm Patterns to have more effective, data-driven conversations about your strategy and architecture.
For a personalized starting point, take our free online assessment. Your results will give you a detailed report on your current maturity and suggest the most relevant patterns to focus on first.
Every Tuesday, we deliver one short, powerful read on AI Native to help you lead better, adapt faster, and build smarter—based on decades of experience helping teams transform for real.